Which metal A is used in thermite process?
The thermite process is a fascinating chemical reaction that has been widely used in various industries for its unique properties. It involves the combination of two substances to produce intense heat and the formation of molten metal. In this article, we will explore the metal that is commonly used in the thermite process and delve into the science behind this remarkable reaction.
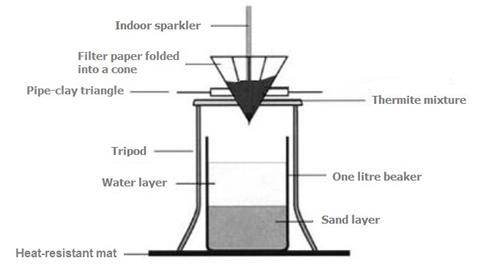
Understanding the Thermite Process
Before we delve into the metal used in the thermite process, let's first gain a basic understanding of how this reaction works. Thermite is a type of exothermic reaction characterized by a highly exothermic oxidation-reduction reaction between metal oxides and a reducing agent, typically a metal powder. The reaction is so highly exothermic that it produces an immense amount of heat, often reaching temperatures exceeding 2500 degrees Celsius (4500 degrees Fahrenheit).
The reaction occurs as follows: when the metal oxide and the reducing agent are mixed together and ignited, the reducing agent strips oxygen from the metal oxide, resulting in the formation of molten metal and the release of a substantial amount of heat. The high temperature generated by the thermite process makes it ideal for applications such as welding, incendiary devices, and even in the field of pyrotechnics.
The Metal of Choice: Aluminum
In the thermite process, the metal that is commonly used as the reducing agent is aluminum. Aluminum is an abundant and versatile metal known for its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and low density. These properties make it a suitable candidate for various applications, including the thermite reaction.
When aluminum powder is combined with a metal oxide, such as iron oxide (Fe2O3), commonly known as rust, a thermite mixture is formed. Iron oxide is often used in thermite reactions due to its stability and availability. When the thermite mixture is ignited, the aluminum reacts with the iron oxide, reducing it to elemental iron while simultaneously producing aluminum oxide as a byproduct. The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Additional reading:How to install Flexible Metal Conduit
What is the purpose of airless spray gun filters?
How do you identify a thrust bearing?
Where do you use a bellows seal gate valve?
What is medical injection molding?
What is the average lifespan of Water Well Drill Pipe?
Top 5 Tips for Selecting a Reliable Longhe Attachment Contractor - Which One Will Ensure Your Project's Success?
2Al + Fe2O3 -> Al2O3 + 2Fe
As the reaction progresses, the intense heat generated causes the iron to melt, resulting in the production of molten iron. The aluminum oxide formed during the reaction acts as a protective layer, preventing further oxidation of the molten iron.
Applications of the Thermite Process
The thermite process finds a wide range of applications across various industries. One of the most notable uses of the thermite reaction is in the field of welding. Thermite welding, also known as thermit welding, is a process where the intense heat generated by the thermite reaction is utilized to join metal parts together. It is particularly useful for welding railway tracks, where a strong and durable bond is essential.
Additionally, the thermite process has been employed in military and defense applications. Thermite-based incendiary devices have been used for their destructive capabilities, as they produce high temperatures and can melt through metal surfaces. The controlled use of thermite mixtures is crucial in applications such as cutting through locks or disabling enemy equipment.
Furthermore, the thermite reaction has found its place in pyrotechnics, where it is utilized to create spectacular displays of light and color. The vibrant sparks and intense heat produced by the thermite reaction make it a popular choice for fireworks and other visual effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the thermite process is a remarkable chemical reaction that harnesses the intense heat generated by the exothermic reaction between a metal oxide and a reducing agent. Aluminum, with its excellent properties, is the metal of choice for the thermite process due to its abundance and effectiveness as a reducing agent. Understanding the science behind the thermite process and its applications in welding, military uses, and pyrotechnics opens up a world of possibilities for this intriguing reaction.
Additional reading:Master Custom Reducer: The Ultimate Solution to Google's Hottest Questions
Everything You Need to Know About Longhe Attachments ODM - The Ultimate Guide
Revolutionizing Train Efficiency with Spiral Bevel Gear?
Roller Bearings: Enhancing Efficiency and Performance in Mechanical Systems
Vibrant and Resilient: The Allure of Color Coated Corrugated Steel Plates
What is the investment casting process?
Investment Casting vs. Die Casting: Which Is Right for Your Application










